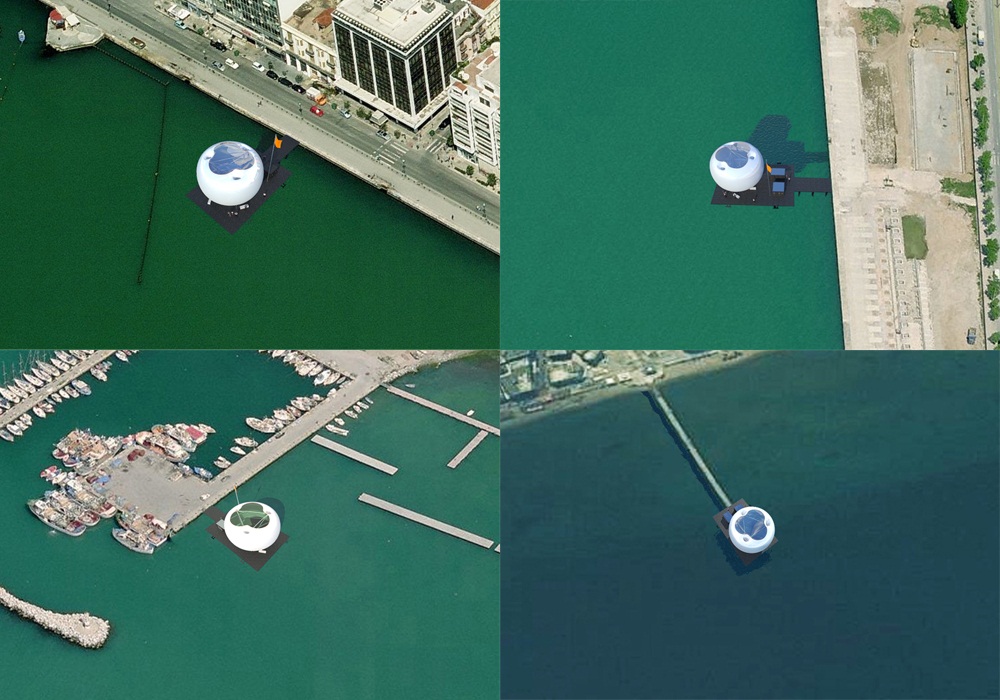
Οι τέσσερις στάσεις του Αρχιτεκτονικού Διαγωνισμού της Αστικής Θαλάσσιας Συγκοινωνίας Θεσσαλονίκης (Πλατεία Ελευθερίας, Μέγαρο Μουσικής, Αρετσού, Περαία) αποτελούνται από τρία στοιχεία: το Δάπεδο, τα Περίπτερα και την Πνευματική Κατασκευή Πεπιεσμένου Αέρα.
Το Δάπεδο οργανώνει τις κινήσεις των χρηστών στο χώρο και παραλαμβάνει το φωτισμό και τα καθιστικά στοιχεία της στάσης. Το Δάπεδο είναι κατασκευασμένο από αδρή ξυλεία εμποτισμένη με ρητίνες στεγάνωσης μαύρου χρώματος, αντίστοιχη με την εμποτισμένη ξυλεία με πίσσα όπως χρησιμοποιείται στην ναυπηγία. Τα καθιστικά στοιχεία της στάσης είναι κατασκευασμένα από φυσικό πέτρωμα. Ο φωτισμός της στάσης αποτελείται από επιδαπέδια φωτιστικά στοιχεία φθορισμού και αλογόνου.
Τα Περίπτερα παραλαμβάνουν τις δημόσιες τουαλέτες και την αποθήκη της στάσης (Α) και το εκδοτήριο εισιτηρίων και το αναψυκτήριο της στάσης (Β). Τα Περίπτερα είναι κατασκευασμένα από μεταλλικό σκελετό υπενδεδυμένο με αδρή ξυλεία (όμοια με του Δαπέδου). Τα κουφώματα των περιπτέρων είναι μεταλλικά πλαίσια υπενδεδυμένα με φύλλα ορείχαλκου όπως χρησιμοποιείται στην ναυπηγία.
Λειτουργικότητα, Οικονομία, Καινοτομία
Προτεραιότητα του σχεδιασμού του Αρχιτεκτονικού Διαγωνισμού της Αστικής Θαλάσσιας Συγκοινωνίας Θεσσαλονίκης είναι η οικονομία, η λειτουργικότητα και η καινοτομία. Η στάση δεν έχει εσωτερικούς χώρους παραμονής. Το κλίμα της Θεσσαλονίκης είναι ήπιο και ο χρόνος παραμονής του χρήστη στη στάση είναι σύντομος. Αυτό επιτρέπει εξοικονόμηση ενέργειας για θέρμανση το χειμώνα και κλιματισμό το καλοκαίρι.
Η ανακλαστική επιφάνεια της Πνευματικής Κατασκευής Πεπιεσμένου Αέρα επιτρέπει την εναρμόνιση της στάσης με τα χαρακτηριστικά της κάθε περιοχής στην οποία τοποθετείται. Τα τρία στοιχεία που αποτελούν κάθε στάση είναι ίδια σε όλες τις στάσεις ώστε να υπάρχει εξοικονόμηση στο σχεδιασμό και την κατασκευή τους και να μπορούν να αναπαραχθούν ως έχουν σε μελλοντικές στάσεις της Αστικής Θαλάσσιας Συγκοινωνίας Θεσσαλονίκης. Επιπρόσθετα η επανάληψή τους ενοποιεί το σύνολο των στάσεων σε όλο το μήκος της διαδρομής της Θαλάσσιας Συγκοινωνίας.
Η κατασκευή της στάσης έχει περιορισμένες απαιτήσεις συντήρησης. Τα στοιχεία της αντικαθίστανται ή επιδιορθώνονται εύκολα και είναι ανθεκτικά στην υγρασία, το θαλασσινό νερό και το βανδαλισμό.
Η Πνευματική Κατασκευή Πεπιεσμένου Αέρα συλλέγει ηλεκτρική ενέργεια και νερό ως εξής:
Η ηλιακή ακτινοβολία εισέρχεται μέσα στην Πνευματική Κατασκευή από την πάνω διαφανή επιφάνειά της. Τα ανακλαστικά πλευρικά τοιχώματα της Πνευματικής Κατασκευής κατευθύνουν την ηλιακή ακτινοβολία προς τις ηλιακές κυψέλες που είναι τοποθετημένες στο εσωτερικό της. Οι ηλιακές κυψέλες μετατρέπουν την ηλιακή ακτινοβολία σε ηλεκτρική ενέργεια. Το προνόμιο της τεχνολογίας αυτής για τη συγκέντρωση ηλιακής ακτινοβολίας έναντι των συμβατικών βαρέων φωτοβολταϊκών στοιχείων από κρύσταλλο και μέταλλο, είναι η δυνατότητα για εκτεταμένη επιφάνεια με ελάχιστο συγκριτικά βάρος. Η τεχνολογία αυτή αναπτύσσεται από πληθώρα εταιριών όπως οι Cool Earth Solar , Emcore , SunPeak Solar , Ausra καθώς και από το πανεπιστήμιο ETH .
Το νερό συλλέγεται από τρία χωνοειδή σημεία στην πάνω επιφάνεια της Πνευματικής Κατασκευής (τα σημεία σύνδεσης των τοιχωμάτων της Πνευματικής Κατασκευής με το μεταλλικό σκελετό της) και κατευθύνεται σε δεξαμενή κάτω από το δάπεδο της στάσης.
Αρχιτέκτονες: Giannikis SHOP
Ομάδα: Σταμάτιος Γιαννίκης (Υπεύθυνος Μελέτης), Εύη Τσάγκα, Στελίνα Τσίφτη, Παναγιώτης Χατζητσακύρης, Γιώργος Αγγέλου
Αγωνοθέτης Διαγωνισμού: Υπουργείο Υποδομών Μεταφορών και Δικτύων (ΥΠΟΜΕΔΙ)
Τοποθεσία: Θεσσαλονίκη, Ελλάδα
Έτος: 2011
Εμβαδόν: 120μ2
EN
Giannikis SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
Floor, Pavilion, Inflated Pneumatic Structure
Four Piers (Eleutherias Square, Megaro, Aretsou, Peraia) were designed for the Architecture Competition for the Thessaloniki Water Transport Piers. Each Pier is composed of three elements: the Floor, the Pavilions and the Inflated Pneumatic Structure.
The Floor arranges the flow of users and incorporates pier lighting and sitting. The Floor is made of rough wood planks treated with tar, a technique used in shipbuilding. Sitting is made of stone blocks. Lighting is integrated in the surface of the Floor.
The Pavilions house the public toilets and storage space (A) and the ticket booth and Pier café (B). The Pavilions are steel structures covered in the same rough wood planks as the Floor. The doors and windows of the Pavilions are made out of brass, another material that references to shipbuilding.
Floor, Pavilion, Inflated Pneumatic Structure
Four Piers (Eleutherias Square, Megaro, Aretsou, Peraia) were designed for the Architecture Competition for the Thessaloniki Water Transport Piers. Each Pier is composed of three elements: the Floor, the Pavilions and the Inflated Pneumatic Structure.
The Floor arranges the flow of users and incorporates pier lighting and sitting. The Floor is made of rough wood planks treated with tar, a technique used in shipbuilding. Sitting is made of stone blocks. Lighting is integrated in the surface of the Floor.
The Pavilions house the public toilets and storage space (A) and the ticket booth and Pier café (B). The Pavilions are steel structures covered in the same rough wood planks as the Floor. The doors and windows of the Pavilions are made out of brass, another material that references to shipbuilding.
The Inflated Pneumatic Structure operates as weather protection and harvests solar energy and water. It is supported by a three column steel structure that holds a triangular ring inside the Inflated Pneumatic Structure. The surface of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure is in constant mechanical support (air supply). The side walls of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure are made of BoPET while the upper and lower walls are made of ETFE . BoPET is a highly reflective synthetic film and ETFE is a transparent synthetic fillm. Both materials have high tensile strength capabilities.
Functionality, Economy, Innovation
The goals of the proposal for the Thessaloniki Water Transport Piers were functionality, economy and innovation.
The Piers have no interior waiting space. The climate of Thessaloniki is mild and the average waiting time for users on the Pier is short. That allows for Pier operation savings in heating during winter and cooling during summer.
The reflective surface of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure integrates the Pier in any surroundings it is positioned. The three elements that compose each Pier are the same everywhere. That allows for savings in design and fabrication as well as the ability for use of the existing Pier design in any future expansion of the Thessaloniki Water Transport Piers in other locations. In addition, the persistence of the same elements throughout the Water Transport System unifies the whole as a single entity.
The Pier construction has low maintenance requirements. All elements are easy to fix or replace and are resistant to humidity, salt water and vandalism.
The goals of the proposal for the Thessaloniki Water Transport Piers were functionality, economy and innovation.
The Piers have no interior waiting space. The climate of Thessaloniki is mild and the average waiting time for users on the Pier is short. That allows for Pier operation savings in heating during winter and cooling during summer.
The reflective surface of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure integrates the Pier in any surroundings it is positioned. The three elements that compose each Pier are the same everywhere. That allows for savings in design and fabrication as well as the ability for use of the existing Pier design in any future expansion of the Thessaloniki Water Transport Piers in other locations. In addition, the persistence of the same elements throughout the Water Transport System unifies the whole as a single entity.
The Pier construction has low maintenance requirements. All elements are easy to fix or replace and are resistant to humidity, salt water and vandalism.
The way the Inflated Pneumatic Structure harvests solar energy and water is the following:
Solar radiation enters the Inflated Pneumatic Structure from its upper transparent wall. The reflective side walls of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure guide the solar beams towards the solar cells that are located in the interior of the Structure. The solar cells transform the solar energy to electricity and store it there. The advantage of this innovative solar cell technology compared to conventional solar cell technology made with steel and glass is the ability for large surfaces with minimal weight. This technology is being developed by a multitude of companies such as Cool Earth Solar , Emcore , SunPeak Solar , Ausra as well as ETH University.
Water is harvested from three cone shaped point at the upper wall of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure (the point of connection between the surface of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure and its steel support ring) and directed towards an under Pier storage facility.
Electricity and water harvested by the Inflated Pneumatic Structure allows for energy and water self-sufficiency of the Pier.
Solar radiation enters the Inflated Pneumatic Structure from its upper transparent wall. The reflective side walls of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure guide the solar beams towards the solar cells that are located in the interior of the Structure. The solar cells transform the solar energy to electricity and store it there. The advantage of this innovative solar cell technology compared to conventional solar cell technology made with steel and glass is the ability for large surfaces with minimal weight. This technology is being developed by a multitude of companies such as Cool Earth Solar , Emcore , SunPeak Solar , Ausra as well as ETH University.
Water is harvested from three cone shaped point at the upper wall of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure (the point of connection between the surface of the Inflated Pneumatic Structure and its steel support ring) and directed towards an under Pier storage facility.
Electricity and water harvested by the Inflated Pneumatic Structure allows for energy and water self-sufficiency of the Pier.
Architect: Giannikis SHOP
Team: Stamatios Giannikis (Team Leader), Evi Tsagka, Stelina, Tsifti, Panagiotis Chatzitsakiris, Giorgos Aggelou
Organizing Committee: Ministry of Infrastructure, Transport and Networks (Greece)
Location: Thessaloniki, Greece
Year: 2011
Size: 120m2
Team: Stamatios Giannikis (Team Leader), Evi Tsagka, Stelina, Tsifti, Panagiotis Chatzitsakiris, Giorgos Aggelou
Organizing Committee: Ministry of Infrastructure, Transport and Networks (Greece)
Location: Thessaloniki, Greece
Year: 2011
Size: 120m2
 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION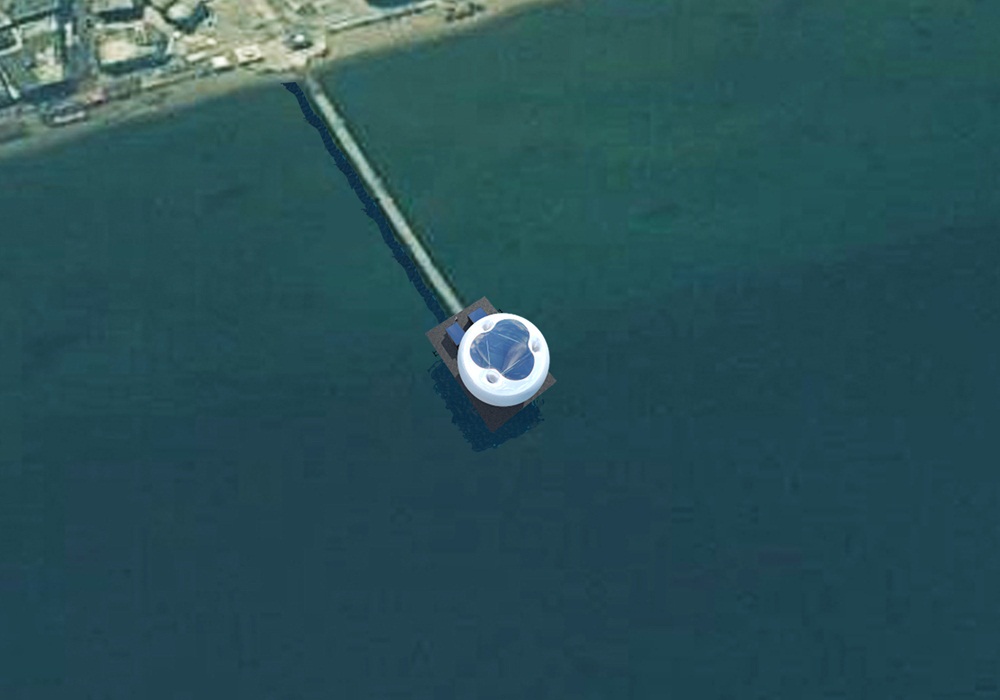 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION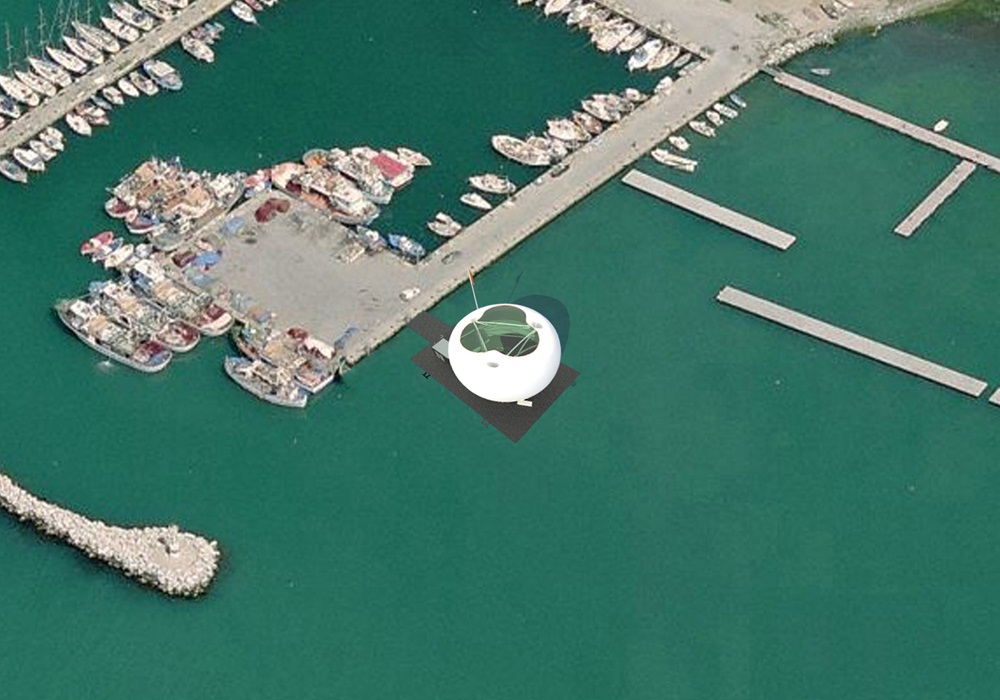 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION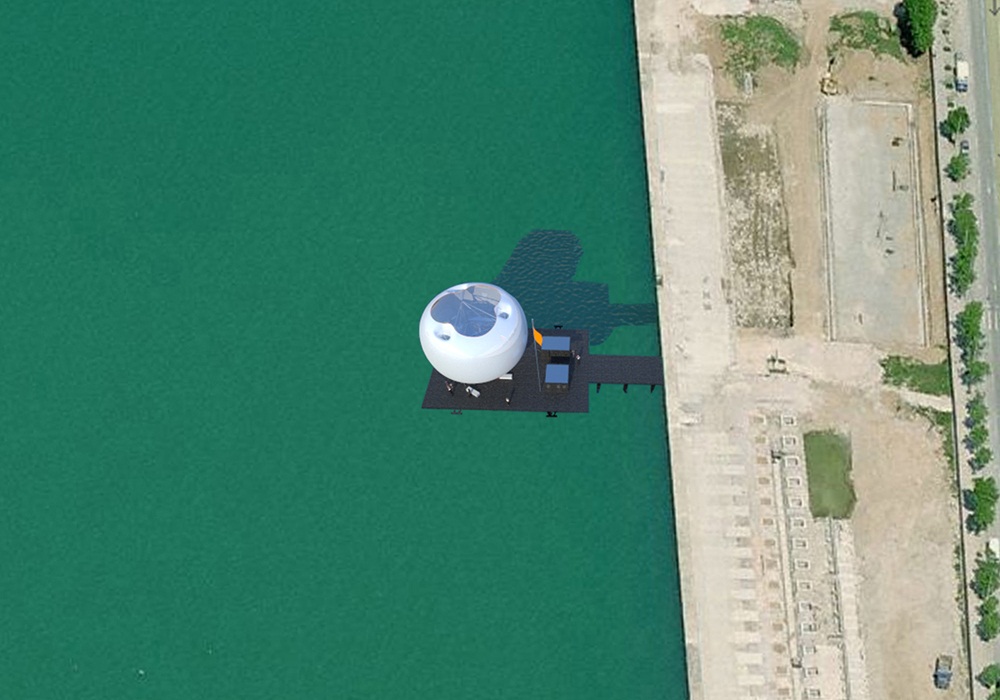 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION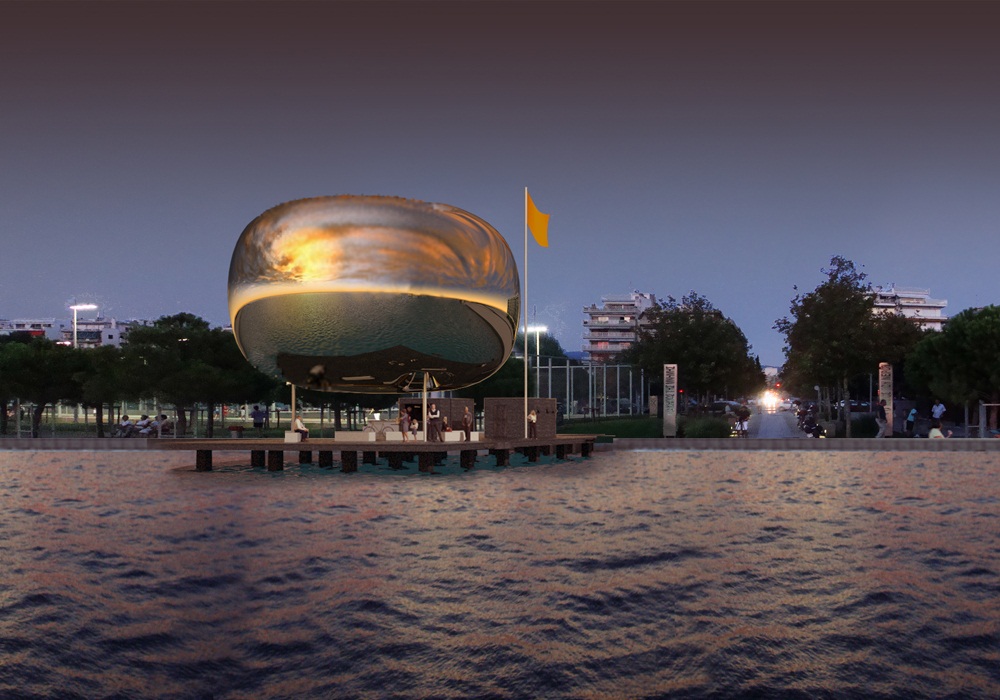 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION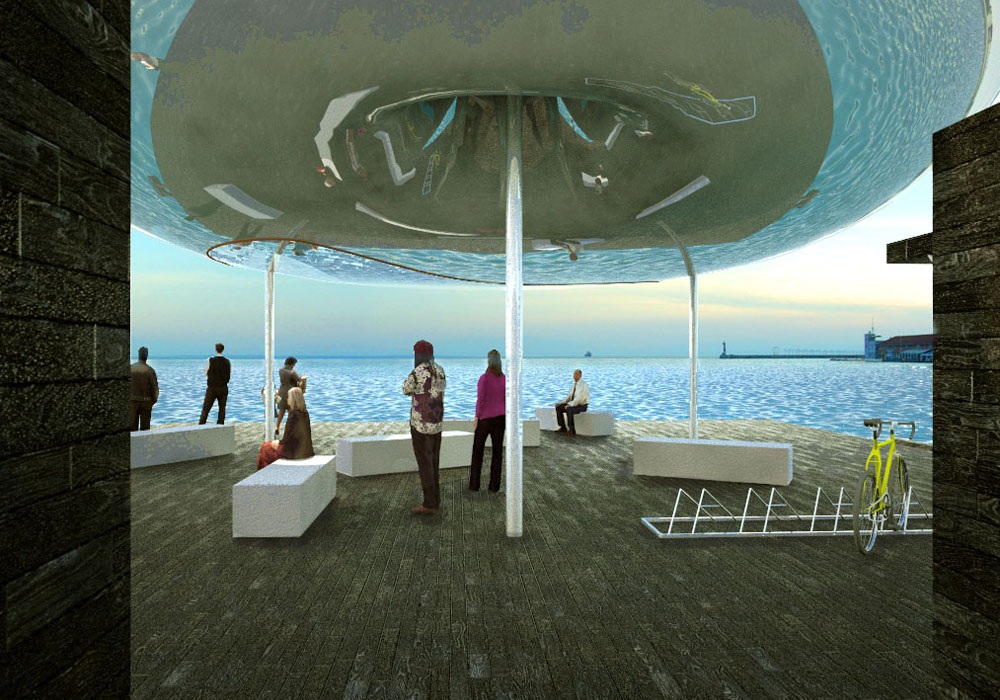 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION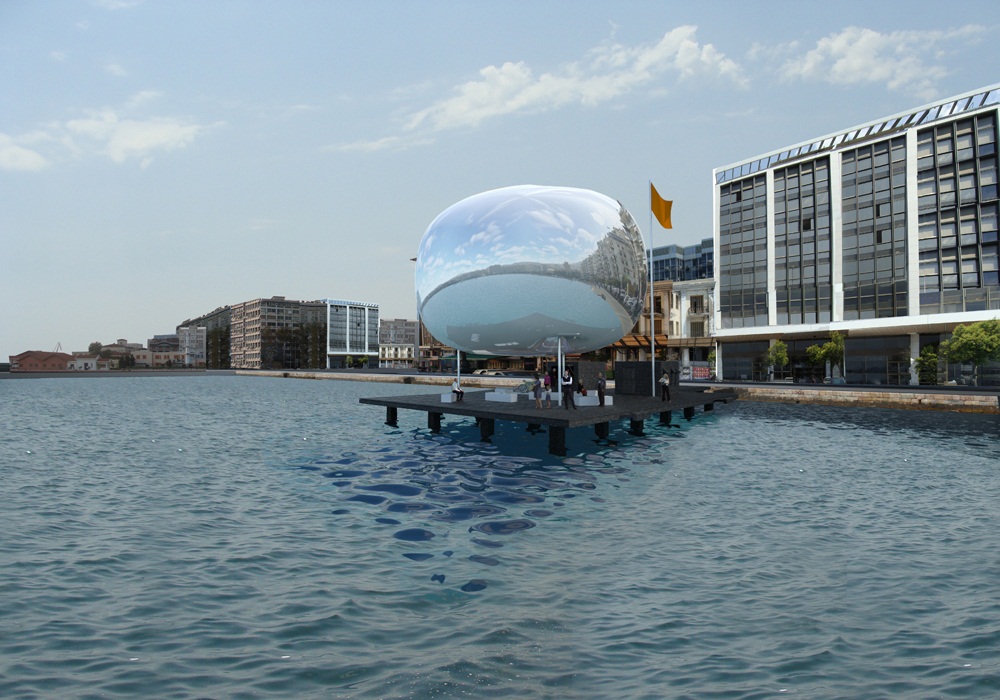 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION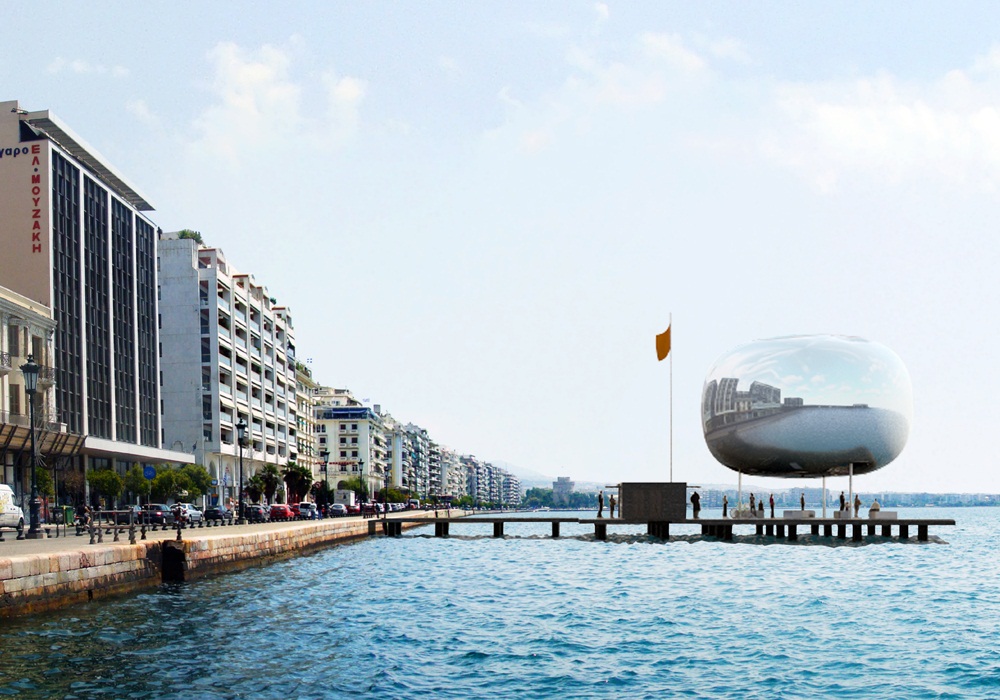 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION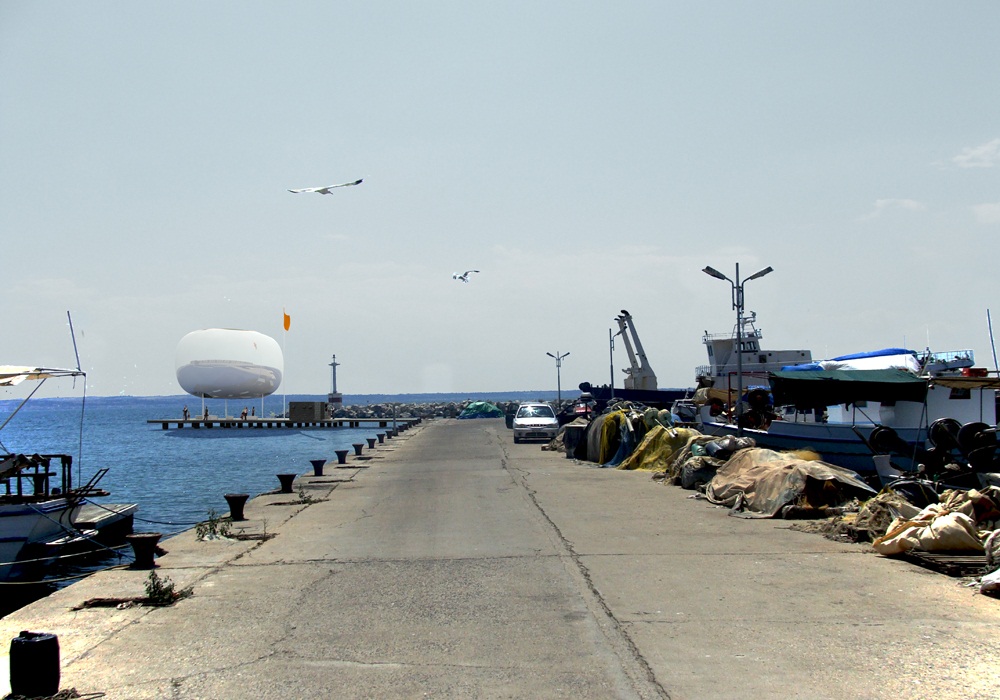 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION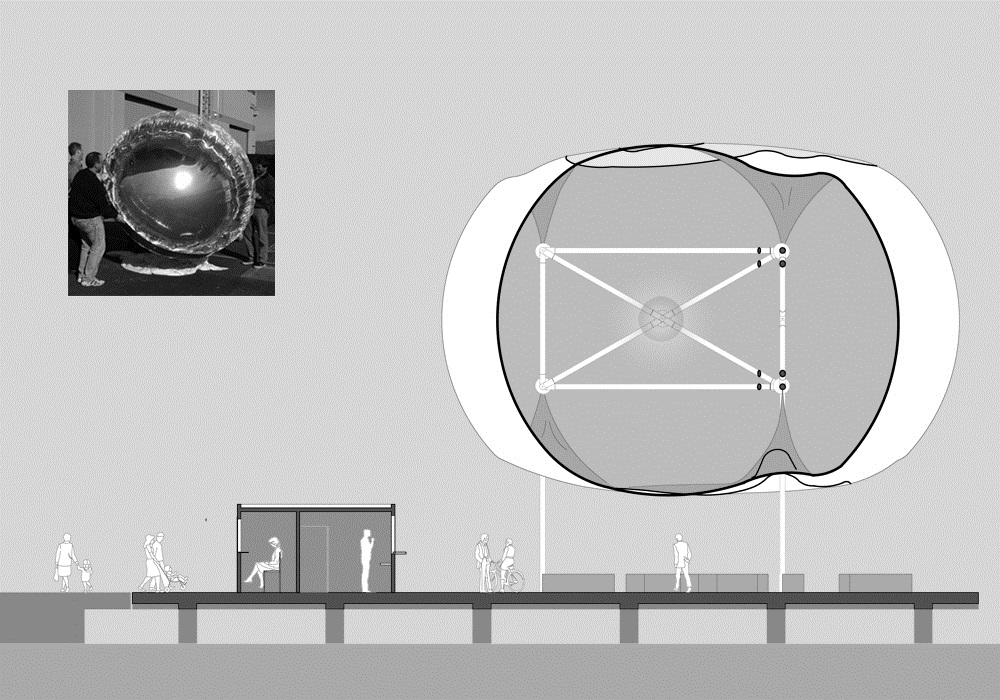 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION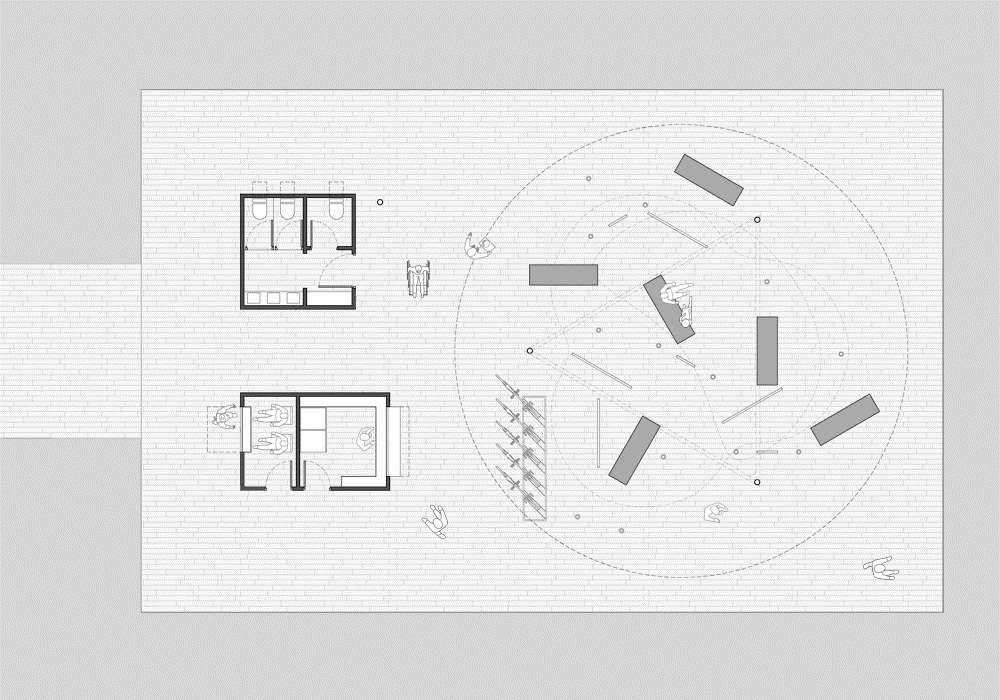 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION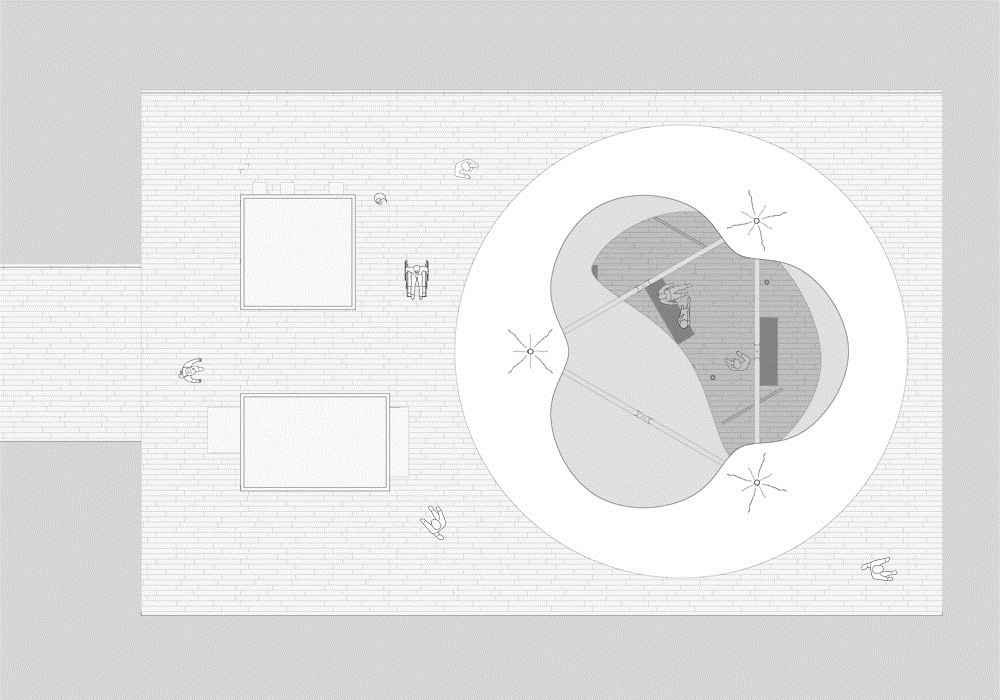 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION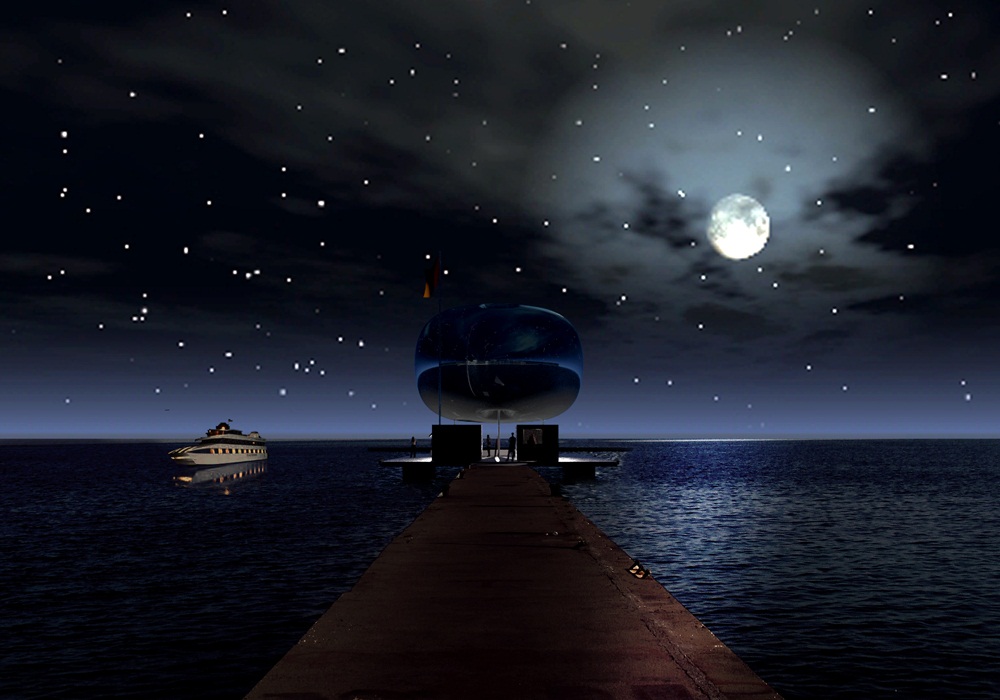 GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITION
GIANNIKIS SHOP / THESSALONIKI WATER TRANSPORT PIERS / HONORARY MENTION IN ARCHITECTURE COMPETITIONREAD ALSO: σχολ(ε)ιο_ ΙΔΙΩΤΙΚΟ ΣΧΟΛΕΙΟ_ΚΑΡΔΙΤΣΑ | ΔΙΟΝΥΣΗΣ ΣΟΤΟΒΙΚΗΣ

